Knowledge Base
Water treatment is as much about knowledge as it is about technology.
At Water Service Elite, we're dedicated to ensuring our clients are always informed. Our FAQ section is a reflection of this commitment, addressing common questions, busting myths, and ensuring that when it comes to water quality, you're always in the know.
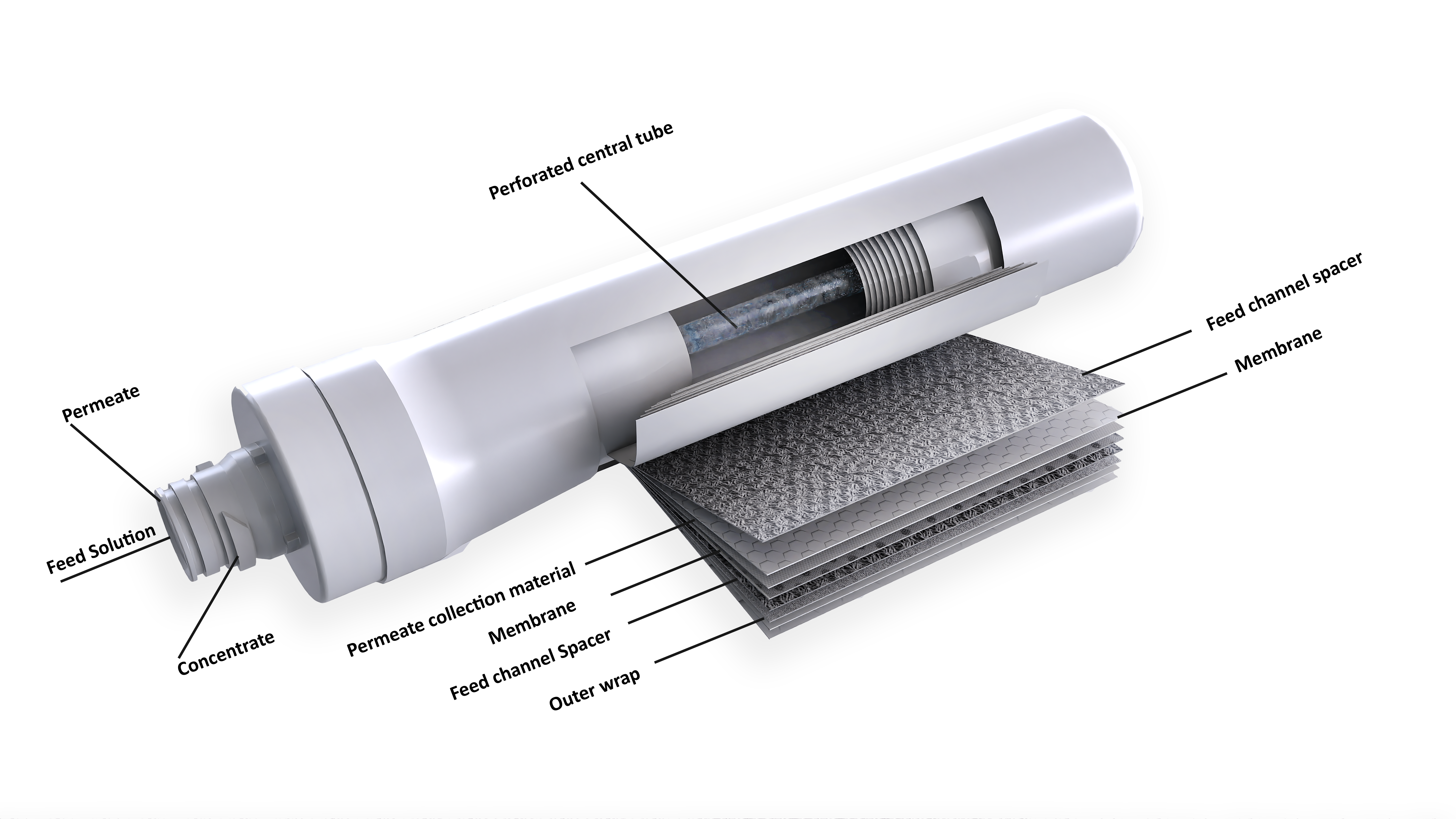
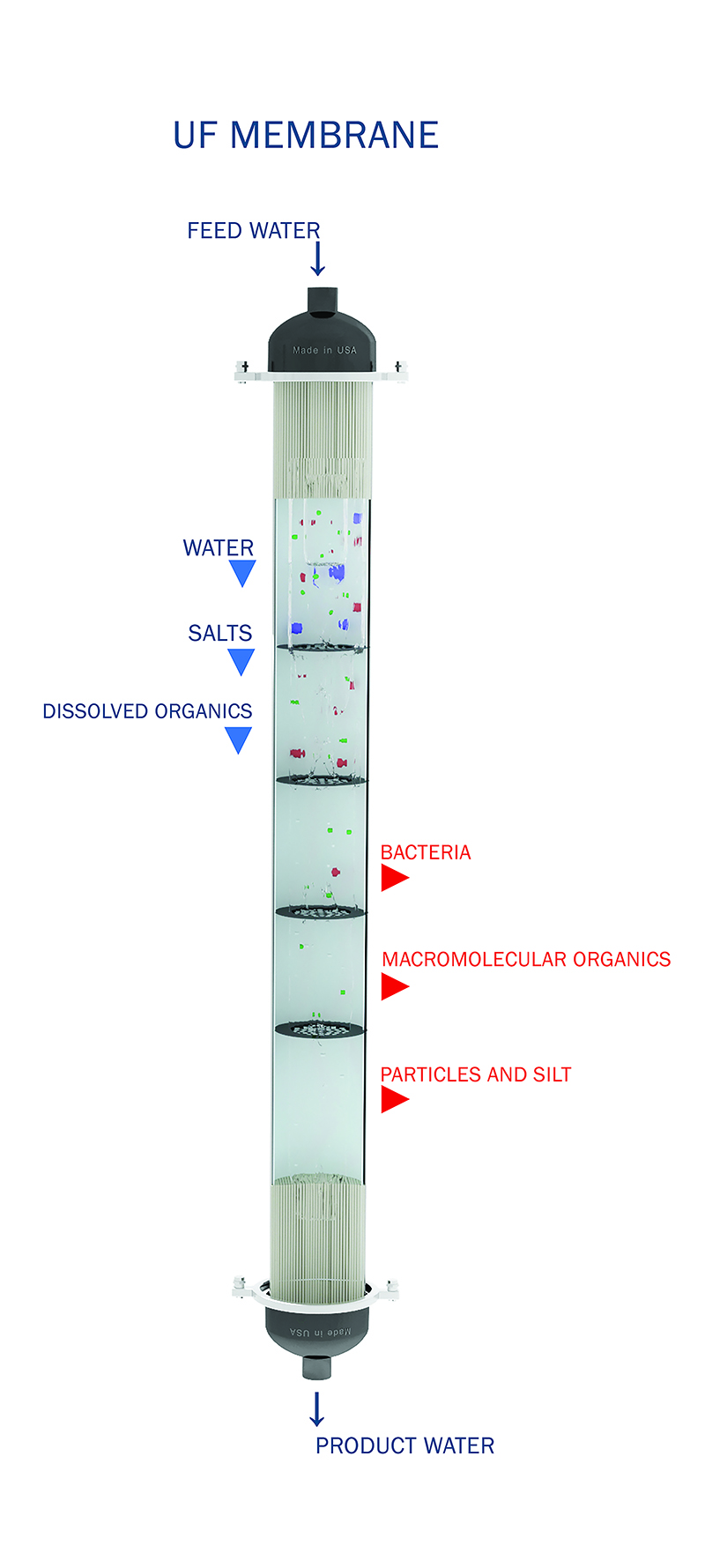 Ultrafiltration uses a membrane with larger pores than RO, allowing it to remove bacteria, viruses, and suspended solids while retaining beneficial minerals. RO, on the other hand, removes nearly all dissolved solids, including salts and minerals, providing a more thorough filtration.
Ultrafiltration uses a membrane with larger pores than RO, allowing it to remove bacteria, viruses, and suspended solids while retaining beneficial minerals. RO, on the other hand, removes nearly all dissolved solids, including salts and minerals, providing a more thorough filtration.
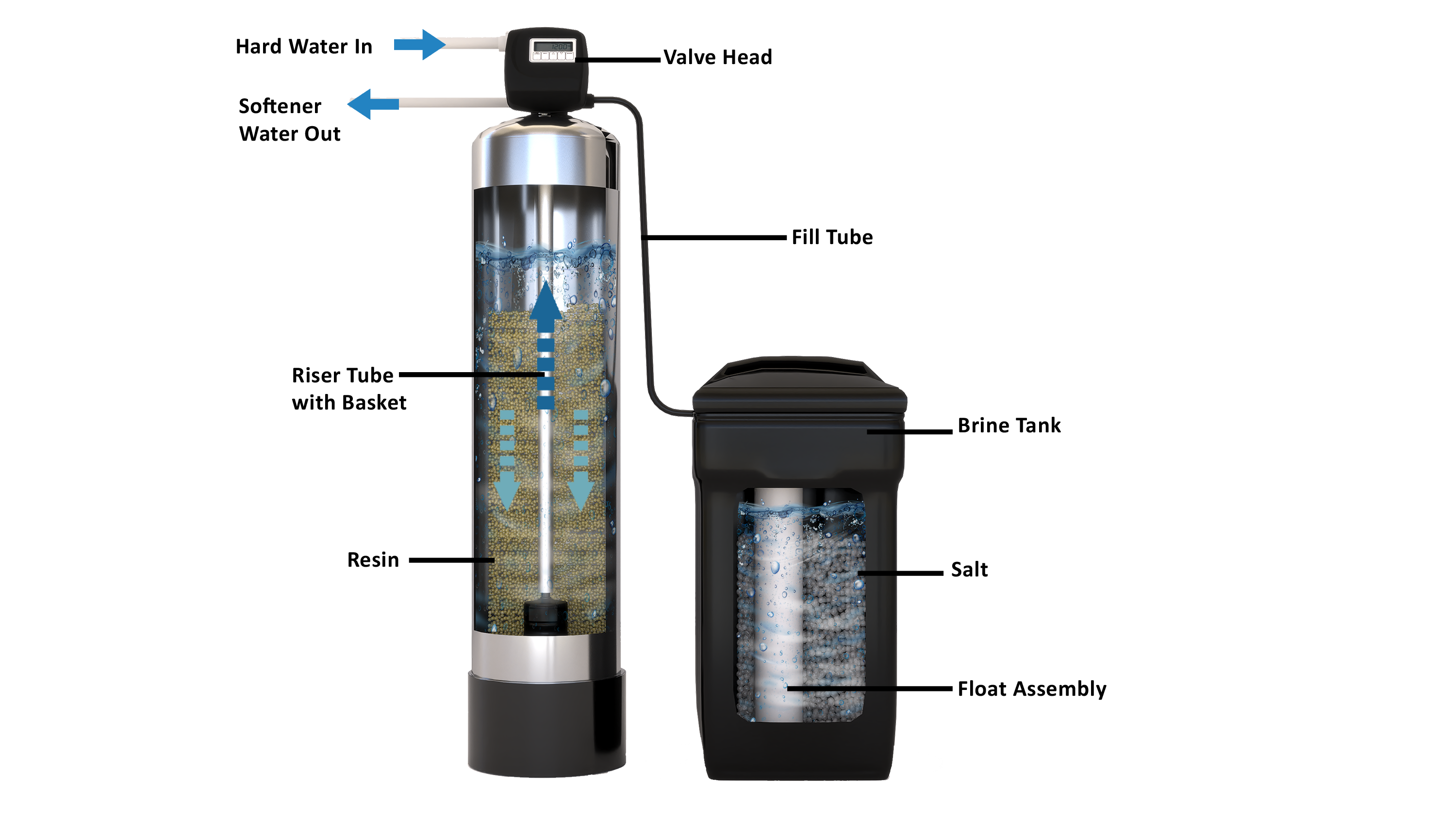 A water softener typically works before the RO system, removing calcium and magnesium to prevent scale buildup on the RO membrane. This combination ensures both the longevity of the RO system and optimal water quality.
A water softener typically works before the RO system, removing calcium and magnesium to prevent scale buildup on the RO membrane. This combination ensures both the longevity of the RO system and optimal water quality.
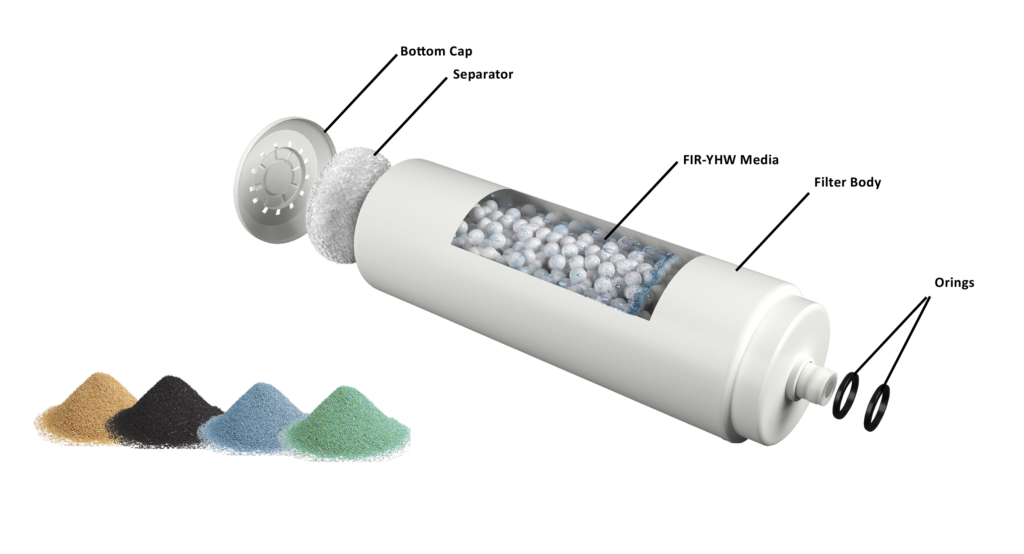 Specialty media can target specific contaminants like iron, manganese, or hydrogen sulfide. For example, KDF media can remove chlorine and heavy metals, while activated alumina can reduce fluoride levels. These media are often used in conjunction with other filtration systems.
Specialty media can target specific contaminants like iron, manganese, or hydrogen sulfide. For example, KDF media can remove chlorine and heavy metals, while activated alumina can reduce fluoride levels. These media are often used in conjunction with other filtration systems.
Deionization (DI) tanks remove mineral ions, including cations like sodium, calcium, iron, and anions like chloride and sulfate. They are commonly used in applications requiring ultra-pure water, such as in laboratories, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing.
Ozonation involves the use of ozone gas (O₃) to disinfect water and remove contaminants. Ozone is a powerful oxidant that can break down organic matter, kill bacteria, viruses, and parasites, and remove unpleasant tastes and odors. Unlike chlorine, ozone leaves no harmful residues, making it an effective and environmentally friendly water treatment method. Ozonation is often used in both commercial and residential systems, particularly in high-end homes where water quality is a priority.
Chemical injection systems are used to introduce chemicals directly into the water supply to address specific water quality issues. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is commonly used to oxidize and remove iron, manganese, and sulfur compounds, which can cause staining and odors. Anti Scale treatments, often involving polyphosphates, are used to prevent scale buildup in pipes and appliances by sequestering calcium and magnesium ions. These systems are particularly useful in regions with problematic water chemistry and are often part of more advanced water treatment setups.
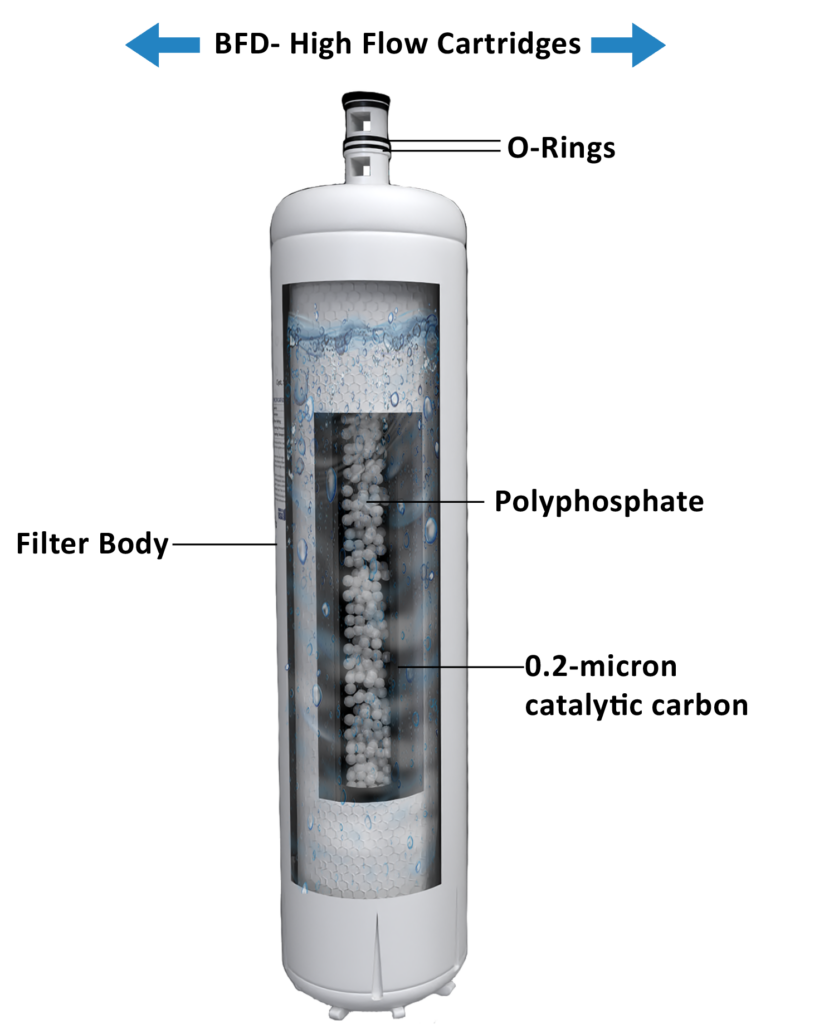 Polyphosphate is an effective anti scale agent that works by binding to minerals like calcium and magnesium in water, preventing them from precipitating and forming scale. This helps protect plumbing systems and water-using appliances from scale buildup, which can reduce efficiency and lead to costly repairs. Polyphosphate treatment is a low-maintenance solution for managing hard water issues, making it ideal for both residential and commercial applications.
Polyphosphate is an effective anti scale agent that works by binding to minerals like calcium and magnesium in water, preventing them from precipitating and forming scale. This helps protect plumbing systems and water-using appliances from scale buildup, which can reduce efficiency and lead to costly repairs. Polyphosphate treatment is a low-maintenance solution for managing hard water issues, making it ideal for both residential and commercial applications.
Deionization (DI) tanks remove dissolved ions from water through a process called ion exchange. The water passes through resin beds that exchange hydrogen and hydroxide ions for cations (e.g., sodium, calcium) and anions (e.g., chloride, sulfate), resulting in high-purity water. DI tanks are commonly used in laboratories, electronics manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and any application where water of extreme purity is required. They are typically integrated into more complex water treatment systems.
When selecting a water filtration system for a commercial property, consider the following factors:
- Water Usage: Determine the volume of water used daily to ensure the system can handle the demand.
- Contaminants: Identify specific contaminants that need to be removed based on water testing.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the system meets local, state, and federal water quality standards.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the ease of maintenance and the availability of service support.
- Scalability: Choose a system that can be expanded or upgraded as your business grows.
- Cost Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including initial investment, maintenance, and operational costs.
 Alkaline filter media work by increasing the pH level of the water, making it more alkaline. These filters often use minerals like magnesium, calcium, and potassium to achieve this effect. Drinking alkaline water is believed to offer several health benefits, such as neutralizing acid in the body, improving hydration, and providing antioxidant properties. While scientific consensus on these benefits varies, many consumers prefer alkaline water for its potential positive effects on overall health.
Alkaline filter media work by increasing the pH level of the water, making it more alkaline. These filters often use minerals like magnesium, calcium, and potassium to achieve this effect. Drinking alkaline water is believed to offer several health benefits, such as neutralizing acid in the body, improving hydration, and providing antioxidant properties. While scientific consensus on these benefits varies, many consumers prefer alkaline water for its potential positive effects on overall health.
A water filtration system improves the taste and odor of water by removing contaminants that cause unpleasant flavors and smells. For example, activated carbon filters can adsorb chlorine, organic compounds, and other chemicals that contribute to bad taste and odor. Systems that include advanced filtration methods, such as Reverse Osmosis or UV treatment, can also remove bacteria and dissolved solids, resulting in clean, fresh-tasting water that is free from any off-putting smells.
- Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) refer to the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances in water, including minerals, salts, and metals. High TDS levels can affect the taste, appearance, and quality of water. Removing TDS is important for applications where water purity is critical, such as in laboratories, aquariums, or high-end residential water systems. Reverse Osmosis is a common method used to reduce TDS, ensuring that the water is clear, pure, and free from unwanted contaminants.
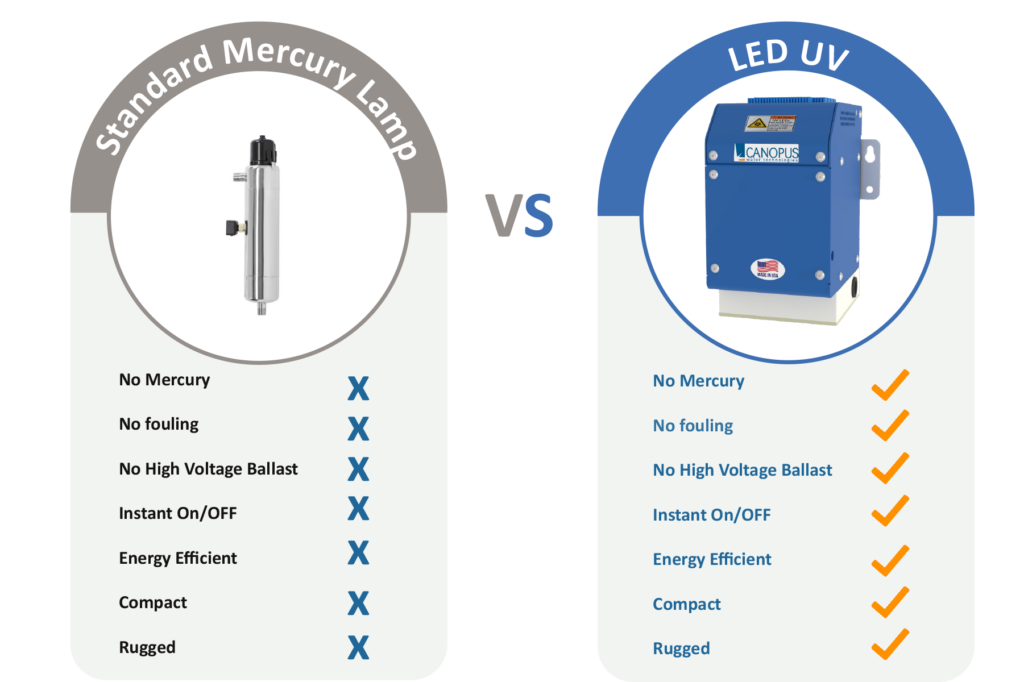
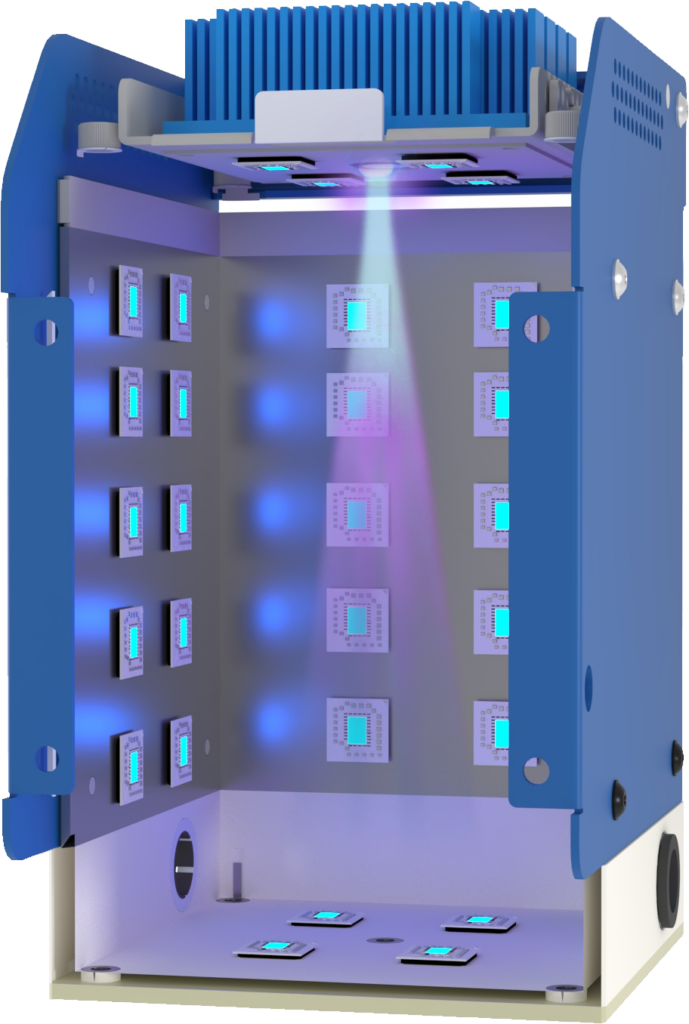 UV water treatment systems use ultraviolet light to disinfect water by inactivating bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. Benefits include:
UV water treatment systems use ultraviolet light to disinfect water by inactivating bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. Benefits include:
- Chemical-Free Disinfection: UV systems provide effective disinfection without the use of chemicals, which can alter water taste and leave residues.
- Energy Efficiency: UV systems are energy-efficient, with low operational costs.
- Environmental Safety: UV treatment does not produce harmful byproducts, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
- Ease of Maintenance: UV systems require minimal maintenance, typically involving only annual bulb replacement.
- Yes, advanced water filtration systems, particularly those that use activated carbon and Reverse Osmosis, are effective at removing many pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from water. PPCPs can enter water supplies through various means, including wastewater. While the levels are usually low, these substances can pose health risks, making it important to remove them from drinking water.
- Fracking, or hydraulic fracturing, is a process used to extract natural gas from deep underground. It has raised concerns about the potential contamination of drinking water with chemicals, heavy metals, and radioactive materials. Water filtration systems, particularly those using Reverse Osmosis and specialized media, can help remove these contaminants, providing an additional layer of protection for those living near fracking sites.
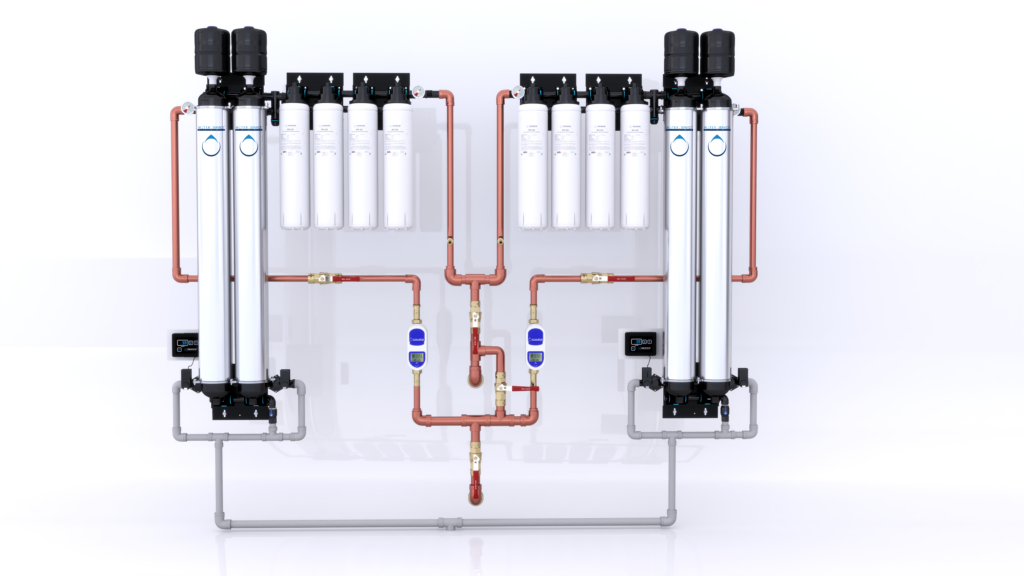 Installing a whole-house water filtration system typically involves the following steps:
Installing a whole-house water filtration system typically involves the following steps:- Site Assessment: A professional technician assesses your home’s plumbing and water quality to determine the best location for the system.
- System Selection: Based on the assessment, the appropriate filtration system is selected to meet your needs.
- Installation: The system is installed at the point where water enters your home, ensuring that all water used in the house is filtered. This process may take several hours, depending on the system's complexity.
- Testing: After installation, the system is tested to ensure it is functioning correctly and that water quality meets the desired standards.
- Point-of-Use (POU): These systems are installed at specific locations where water is used, such as under a sink or at a specific faucet. They are ideal for filtering drinking and cooking water.
- Point-of-Entry (POE): These systems are installed at the main water line where water enters the home or building. They filter all the water used throughout the property, including for bathing, laundry, and other purposes. POE systems are suitable for addressing widespread water quality issues like hard water or contaminants affecting the entire water supply.
 Integrating a water filtration system into an existing commercial infrastructure involves several steps:
Integrating a water filtration system into an existing commercial infrastructure involves several steps:- Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the current water system, including usage patterns and specific water quality concerns.
- Customization: Design a filtration system that addresses the unique needs of the business, whether it’s for manufacturing, food service, or another application.
- Installation: Install the filtration system with minimal disruption to operations, ensuring it complements the existing infrastructure.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Implement a monitoring and maintenance plan to ensure the system continues to meet water quality requirements.
- Specialty filtration media are tailored to remove specific contaminants, making them highly effective in commercial applications where water quality needs are unique. For example:
- Activated Alumina: Used for fluoride and arsenic removal.
- KDF (Kinetic Degradation Fluxion): Removes heavy metals like lead and mercury.
- Ion Exchange Resins: Target specific ions for softening or deionization purposes.
- Greensand: Removes iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide.
- These media can be combined within a filtration system to address multiple contaminants, ensuring that the water meets stringent quality standards required in various industries.
Hydrogen peroxide systems inject H2O2 into the water, where it acts as a powerful oxidizer. This process effectively removes iron, manganese, and sulfur compounds by converting them into solid particles that can be filtered out. H2O2 is also effective at killing bacteria and neutralizing odors. These systems are often used in well water applications or in areas where these contaminants are particularly problematic.
- When selecting a water filtration system for a high-end home, consider:
Water Quality: Conduct a comprehensive water analysis to identify specific contaminants, including chemicals, heavy metals, and biological impurities, as well as hard water issues that may affect the home.
- Aesthetic Preferences: Consider systems that not only provide excellent water quality but also align with the home’s design and plumbing setup. Some high-end systems are designed to be discreet and integrate seamlessly into luxury homes.
- System Capacity: Ensure the system can handle the water usage demands of a large property, including multiple bathrooms, kitchens, and any additional features like pools or spas.
- Advanced Features: Look for systems with advanced features such as real-time monitoring, automated maintenance alerts, and remote control via smartphone apps. High-end homes often benefit from systems that offer a blend of convenience, automation, and top-tier performance.
- Maintenance and Support: Opt for systems that come with professional maintenance services and support, ensuring that the system remains in peak condition without requiring the homeowner to manage complex upkeep.
Health Benefits: If health is a priority, consider systems that offer additional benefits, such as alkaline water filters, to provide enhanced hydration and antioxidant properties.
- Maintaining a commercial water filtration system involves regular monitoring and servicing to ensure optimal performance and compliance with health and safety standards. Key considerations include:
- Filter Replacement: Schedule regular filter changes based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and water quality conditions. In high-demand settings, this might be more frequent.
- System Inspections: Conduct periodic inspections to check for any signs of wear, leaks, or system malfunctions that could compromise water quality.
- Water Quality Testing: Regular testing is essential to ensure that the system continues to meet the required water quality standards. This is particularly important in industries where water quality is critical, such as food service or pharmaceuticals.
- Scaling and Fouling Prevention: In areas with hard water, implement additional measures such as antiscalant injections or softening to prevent scaling, which can damage equipment and reduce efficiency.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, water quality tests, and any system repairs or upgrades to ensure traceability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Chemical injection for anti scaling involves the use of specific chemicals, often polyphosphates or antiscalants, that are injected into the water supply to prevent scale formation. These chemicals work by binding to calcium and magnesium ions, which are the primary causes of scale, and keeping them in solution so they don’t precipitate and form deposits on pipes, heating elements, or other equipment. This is particularly important in industries that use high-temperature water or steam, as scale can significantly reduce efficiency and lead to costly repairs.
- Ensuring compliance with local and federal regulations involves several key steps:
- Understand the Regulations: Stay informed about the water quality standards and regulations that apply to your area. This includes EPA standards for drinking water, state-specific guidelines, and any local ordinances that might affect your system.
- Regular Testing: Conduct regular water quality tests to ensure your system meets or exceeds the required standards. This is especially important in commercial settings where water quality can directly impact public health.
- Proper Documentation: Keep thorough records of all water tests, maintenance activities, and any changes or upgrades to your system. This documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance during inspections or audits.
- Work with Certified Professionals: Ensure that your system is installed and maintained by certified professionals who are familiar with regulatory requirements. They can provide valuable guidance and ensure that your system is up to code.
- Stay Updated: Regulations can change, so it’s important to stay updated on any new requirements or recommendations that may impact your water filtration system.